Product Description
Product Description
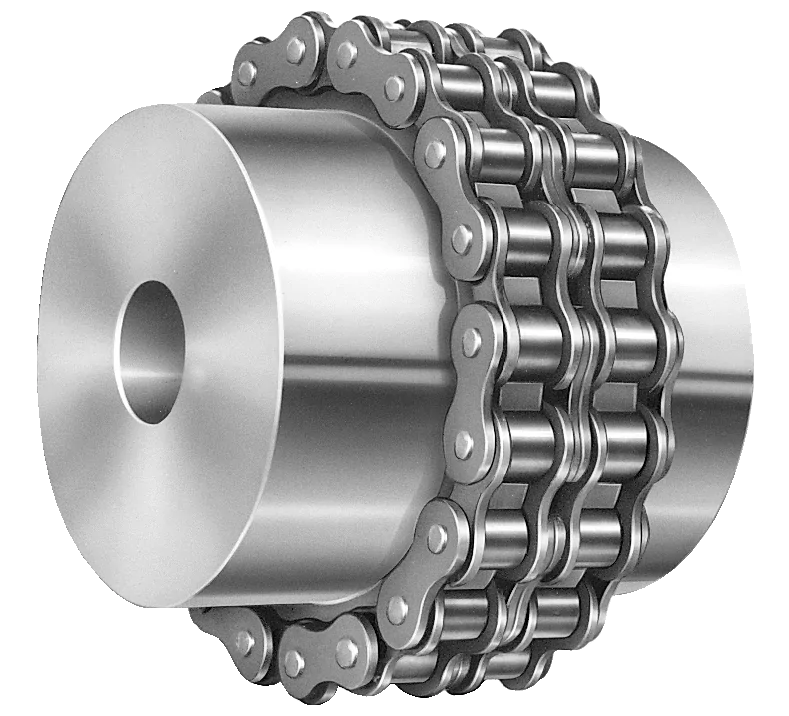
Roller chain couplings have the advantages of simple structure, convenient loading and unloading, large torque transmission, and easy operation. However, there is significant wear between the chains, especially during high-speed operation when the radial motion generated by centrifugal force will accelerate their wear. Therefore, it is not suitable for use at high speeds and under impact loads, nor for the connection of vertical shafts.
When designing the overall structure of the coupling, full attention should be paid to the lubrication and dust prevention between the tooth surface and the rollers, and an outer shell should be added. In addition to dust and oil storage, it also has a protective effect. Because if the chain breaks, it may cause personal accidents.
The double row sleeve roller chain coupling has formed a standard (old standard GB6069-85, new standard GB/T 6069-2002). The transmission torque and allowable speed are 4 times and 2 times that of a single row roller chain of the same size, respectively. Because when the chain size is determined, it can accommodate 2 teeth within the width of a single row of sleeve rollers, while a double row can only accommodate 1 tooth, the tooth thickness of a single row is only half of that of a double row. So, the rollers of the double row chain are located in the grooves of the main and driven sprockets, and when subjected to force, they rotate independently without interfering with each other, reducing wear.
Product Parameters
| model | Nominal torqueTnN·m | Allowable speed(n) r/min |
Axis hole diameter d1,d2 |
Axis hole length | Chain number | chain Pitch |
Number of teeth Z |
D | b1 | S | A | Dx () |
Lx () |
kg | Transmission inertiakg·m2 | ||
| Ymodel | J1model | ||||||||||||||||
| No cover installed | Installing cover | L | L1 | ||||||||||||||
| GL1 | 40 | 1400 | 4500 | 16 | 42 | – | 06B | 9.525 | 14 | 51.06 | 5.3 | 4.9 | – | 70 | 70 | 0.40 | 0.0571 |
| 18 | 42 | – | – | ||||||||||||||
| 19 | 42 | – | – | ||||||||||||||
| 20 | 52 | 38 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| GL2 | 63 | 1250 | 4500 | 19 | 42 | – | 06B | 9.525 | 16 | 57.08 | 5.3 | 4.9 | – | 75 | 75 | 0.70 | 0.0571 |
| 20 | 52 | 38 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| 22 | 52 | 38 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| 24 | 52 | 38 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| GL3 | 100 | 1000 | 4000 | 20 | 52 | 38 | 08B | 12.7 | 14 | 68.88 | 7.2 | 6.7 | 12 | 85 | 80 | 1.1 | 0.00038 |
| 22 | 52 | 38 | 12 | ||||||||||||||
| 24 | 52 | 44 | 12 | ||||||||||||||
| 25 | 62 | – | 6 | ||||||||||||||
| GL4 | 160 | 1000 | 4000 | 24 | 52 | – | 08B | 12.7 | 16 | 76.91 | 7.2 | 6.7 | – | 95 | 88 | 1.8 | 0.0 |
| 25 | 62 | 44 | 6 | ||||||||||||||
| 28 | 62 | 44 | 6 | ||||||||||||||
| 30 | 82 | 60 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 32 | 82 | 60 | – | ||||||||||||||
| GL5 | 250 | 800 | 3150 | 28 | 62 | – | 10A | 15.875 | 16 | 94.46 | 8.9 | 9.2 | – | 112 | 100 | 3.2 | 0.0571 |
| 30 | 82 | 60 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 32 | 82 | 60 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 35 | 82 | 60 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 38 | 82 | 60 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 40 | 112 | 84 | – | ||||||||||||||
| GL6 | 400 | 630 | 2500 | 32 | 82 | 60 | 10A | 15.875 | 20 | 116.57 | 8.9 | 9.2 | – | 140 | 105 | 5.0 | 0.0058 |
| 35 | 82 | 60 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 38 | 82 | 60 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 40 | 112 | 84 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 42 | 112 | 84 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 45 | 112 | 84 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 18 | 112 | 84 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 50 | 112 | 84 | – | ||||||||||||||
| GL7 | 630 | 630 | 2500 | 40 | 112 | 60 | 12A | 19.05 | 18 | 127.78 | 11.9 | 10.9 | – | 150 | 122 | 7.4 | 0.012 |
| 42 | 112 | 60 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 45 | 112 | 60 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 48 | 112 | 84 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 50 | 112 | 84 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 55 | 112 | 84 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 60 | 142 | 107 | – | ||||||||||||||
| GL8 | 1000 | 500 | 2240 | 45 | 112 | 84 | 16A | 25.40 | 16 | 154.33 | 15.0 | 14.3 | 12 | 180 | 135 | 11.1 | 0.571 |
| 48 | 112 | 84 | 12 | ||||||||||||||
| 50 | 112 | 84 | 12 | ||||||||||||||
| 55 | 112 | 84 | 12 | ||||||||||||||
| 60 | 142 | 107 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 65 | 142 | 107 | – | ||||||||||||||
| 70 | 142 | 107 | – | ||||||||||||||
| GL9 | 1600 | 400 | 2000 | 50 | 112 | 84 | 16A | 25.4 | 20 | 186.50 | 15.0 | 14.3 | 12 | 215 | 145 | 20.0 | 0.061 |
| 55 | 112 | 84 | 12 | ||||||||||||||
Packaging & Shipping
After Sales Service
If during transportation or if the customer receives the goods, opens the packaging and finds any damage, they can resend a new product to the customer.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can chain couplings transmit both torque and linear motion?
No, chain couplings are primarily designed to transmit torque between rotating shafts and are not intended for transmitting linear motion. The main function of a chain coupling is to connect two shafts in order to transfer rotational power from one shaft to another.
Chain couplings achieve torque transmission through the engagement of the roller chain with the sprockets on the connected shafts. As the driving sprocket rotates, it imparts rotational motion to the chain, which in turn rotates the driven sprocket connected to the other shaft. This mechanism allows the torque to be transmitted from one shaft to the other.
However, chain couplings do not provide a means for converting or transmitting linear motion. They are not designed to handle axial displacement or linear forces. Attempting to use a chain coupling for transmitting linear motion would result in inefficient and unreliable operation, as the coupling is not designed to handle the specific requirements and forces associated with linear motion.
For applications that require the transmission of linear motion, there are other types of couplings specifically designed for this purpose. Examples include rack and pinion systems, linear couplings, or specialized linear motion couplings that incorporate mechanisms such as ball screws or lead screws. These couplings are designed to convert rotary motion into linear motion or to transmit linear forces directly.
It is important to select the appropriate coupling type based on the specific requirements of the application, whether it involves torque transmission or the transmission of linear motion. Consulting the manufacturer’s specifications, guidelines, or seeking expert advice can help ensure the correct coupling selection for a particular application.
What is the maximum torque capacity of a chain coupling?
The maximum torque capacity of a chain coupling can vary depending on several factors, including the size and design of the coupling, the type and quality of the components used, and the application requirements. It is important to refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines for the specific chain coupling being used. These specifications typically provide the maximum torque capacity or the maximum allowable torque for the coupling.
The maximum torque capacity is usually expressed in torque units, such as Newton-meters (Nm) or foot-pounds (ft-lb). It represents the maximum amount of torque that the chain coupling can transmit without exceeding its design limits or risking premature failure.
When selecting a chain coupling, it is crucial to consider the torque requirements of the application and choose a coupling with a sufficient torque capacity. Factors such as the power requirements, operating conditions, and misalignment tolerance should be taken into account to ensure that the selected coupling can handle the required torque.
It is important to note that exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a chain coupling can lead to various issues, including accelerated wear, excessive stress on the components, and potential coupling failure. Therefore, it is recommended to always operate the chain coupling within its specified torque limits to maintain its reliability and longevity.
For accurate and precise information regarding the maximum torque capacity of a specific chain coupling, it is necessary to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or contact the manufacturer directly. They can provide detailed information based on the specific design and specifications of the coupling.

What is a chain coupling?
A chain coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two rotating shafts in a power transmission system. It consists of two sprockets or toothed wheels and a roller chain that meshes with the sprocket teeth. The sprockets are mounted on the respective shafts and linked together by the chain, allowing torque to be transmitted from one shaft to the other.
Chain couplings are designed to provide a flexible and reliable connection between shafts while accommodating misalignment between them. They are known for their ability to compensate for angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
The sprockets of a chain coupling typically have hardened teeth that engage with the rollers of the chain. The chain itself is made up of a series of interconnected links, each consisting of two plates joined by pins. The rollers are mounted on the pins, allowing them to rotate freely and mesh with the sprocket teeth.
One of the key advantages of chain couplings is their ability to transmit high torque loads. The engagement between the sprockets and the chain provides a positive drive, allowing for efficient power transfer even in demanding applications. Chain couplings are commonly used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment where large amounts of power need to be transferred, such as conveyors, mixers, crushers, and industrial drives.
Chain couplings also offer flexibility in shaft alignment. They can compensate for angular misalignment, which occurs when the shafts are not perfectly aligned at an angle. Additionally, they can accommodate parallel misalignment, where the shafts are offset from each other, as well as axial misalignment, which refers to the displacement along the axis of the shafts.
Proper lubrication is essential for the efficient operation and longevity of chain couplings. Lubricants such as oil or grease are applied to the chain and sprockets to reduce friction and wear. This helps to prevent heat buildup and ensures smooth rotation and power transmission.
Chain couplings are available in various sizes, configurations, and materials to suit different application requirements. The selection of a chain coupling depends on factors such as torque capacity, speed, shaft diameter, and misalignment tolerance.
In summary, chain couplings provide a flexible, reliable, and high-torque solution for connecting rotating shafts in power transmission systems. They offer the ability to compensate for misalignment, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications where efficient power transfer is crucial.


editor by CX 2024-03-14
